Researchers Uncover WatchGuard VPN Bug That Could Let Attackers Take Over Devices
Cybersecurity researchers have disclosed details of a recently patched critical security flaw in WatchGuard Fireware that could allow unauthenticated attackers to execute arbitrary code.
The vulnerability, tracked as CVE-2025-9242 (CVSS score: 9.3), is described as an out-of-bounds write vulnerability affecting Fireware OS 11.10.2 up to and including 11.12.4_Update1, 12.0 up to and including 12.11.3 and 2025.1.
"An out-of-bounds write vulnerability in the WatchGuard Fireware OS iked process may allow a remote unauthenticated attacker to execute arbitrary code," WatchGuard said in an advisory released last month. "This vulnerability affects both the mobile user VPN with IKEv2 and the branch office VPN using IKEv2 when configured with a dynamic gateway peer."
It has been addressed in the following versions –
- 2025.1 – Fixed in 2025.1.1
- 12.x – Fixed in 12.11.4
- 12.3.1 (FIPS-certified release) – Fixed in 12.3.1_Update3 (B722811)
- 12.5.x (T15 & T35 models) – Fixed in 12.5.13)
- 11.x – Reached end-of-life
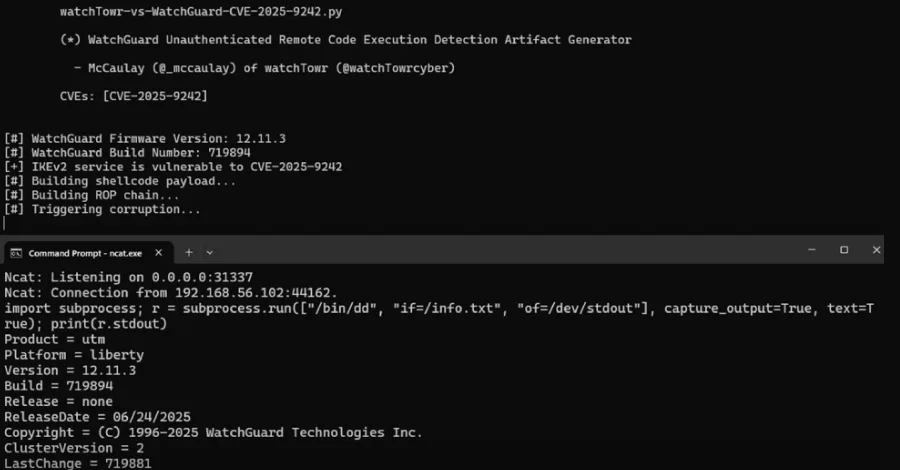
A new analysis from watchTowr Labs has described CVE-2025-9242 as "all the characteristics your friendly neighbourhood ransomware gangs love to see," including the fact that it affects an internet-exposed service, is exploitable sans authentication, and can execute arbitrary code on a perimeter appliance.
The vulnerability, per security researcher McCaulay Hudson, is rooted in the function "ike2_ProcessPayload_CERT" present in the file "src/ike/iked/v2/ike2_payload_cert.c" that's designed to copy a client "identification" to a local stack buffer of 520 bytes, and then validate the provided client SSL certificate.
The issue arises as a result of a missing length check on the identification buffer, thereby allowing an attacker to trigger an overflow and achieve remote code execution during the IKE_SA_AUTH phase of the handshake process used to establish a virtual private network (VPN) tunnel between a client and WatchGuard's VPN service via the IKE key management protocol.
"The server does attempt certificate validation, but that validation happens after the vulnerable code runs, allowing our vulnerable code path to be reachable pre-authentication," Hudson said.
WatchTowr noted that while WatchGuard Fireware OS lacks an interactive shell such as "/bin/bash," it's possible to for an attacker to weaponize the flaw and gain control of the instruction pointer register (aka RIP or program counter) to ultimately spawn a Python interactive shell over TCP by leveraging an mprotect() system call, effectively bypassing NX bit (aka no-execute bit) mitigations.
Once the remote Python shell, the foothold can be escalated further through a multi-step process to obtain a full Linux shell –
- Directly executing execve within Python in order to remount the filesystem as read/write
- Downloading a BusyBox busybox binary onto the target
- Symlinking /bin/sh to the BusyBox binary
The development comes as watchTowr demonstrated that a now-fixed denial-of-service (DoS) vulnerability impacting Progress Telerik UI for AJAX (CVE-2025-3600, CVSS score: 7.5) can also enable remote code execution depending on the targeted environment. The vulnerability was addressed by Progress Software on April 30, 2025.
"Depending on the target codebase – for example, the presence of particular no-argument constructors, finalizers, or insecure assembly resolvers – the impact can escalate to remote code execution," security researcher Piotr Bazydlo said.
Earlier this month, watchtower's Sina Kheirkhah also shed light on a critical pre-authenticated command injection flaw in Dell UnityVSA (CVE-2025-36604, CVSS score: 9.8/7.3) that could result in remote command execution. Dell remediated the vulnerability in July 2025 following responsible disclosure on March 28.
Found this article interesting? Follow us on Google News, Twitter and LinkedIn to read more exclusive content we post.
Original Article Published at The Hackers News
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________